“Very stimulating couple of days at #kmuk – insights into gamification, perspectives on engagement & mulling over global individual concept”
This quote from one of the presenters was a great way to end what was a really enjoyable and rewarding couple of days at the 11th KMUK held a few weeks back. Despite sharing chairing duties with David Gurteen I managed to capture much of the social media activity on Day One and publish a series of Storify accounts. On Day Two I upped the informality and attempted to broaden the gamification debate with Andrzej Marzcewski.
A lot of ‘Operational KM’ activities emerged but I will focus on presentations from Alim Khan who outlined a very interesting technique in co-creating a report (writeshops), gamification session with Andrzej and an energetic performance from Patricia Eng on the US Nuclear industry’s knowledge capture and retention programme.
Knowledge Capture & Retention in the US Nuclear Industry – a story of passion!
So Ladies first, here’s a few of the comments Patricia made:
You have to make the exec management think you are serving them but you are serving the workforce
Don’t worry if you don’t have much money, what you need is PASSION, hang about the cafe. Replaces the old smokers room.
KM metrics? Ask the problem owner, help them develop the tools, go back and see if things are better
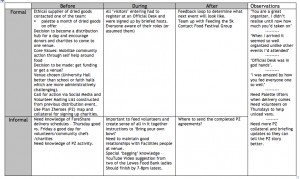
 The slide that caught my eye though was this one. Apart from the fact that Patricia’s efforts save $37m she rightly focused on the pain points one of which was around departing knowledge. It was a theme that came back a number of times and Patricia’s work inspired a similar exercise at Lloyds Register.
The slide that caught my eye though was this one. Apart from the fact that Patricia’s efforts save $37m she rightly focused on the pain points one of which was around departing knowledge. It was a theme that came back a number of times and Patricia’s work inspired a similar exercise at Lloyds Register.
Patricia believes people who leave have different motivations for sharing what they know before the leave even if their departure is involuntary. I would group them into the following categories:
- Legacy/Notoriety: I want what I’ve done in the organisation to be remembered and passed on;
- Avarice: I want my cv to reflect what I’ve done and I see this process and the stories it generates helping me as a freelancer.
In fact this ‘What’s in it for me’ motivational issue is often overlooked by many KM’ers and is one of the core foundations of the work I am doing in Iran with Ron Young. And here’s where I disagree with many in the KM community who are convinced that if you get the culture right then knowledge sharing naturally occurs: There has to be something in it for people to be willing to share what they know.
A study in collaboration at the World Health Organisation
Dr Alim Khan is an incredibly well educated individual who thrives on complexity and with whom I had the good fortune of spending two weeks in Darfur as part of a mission to see how KM might be grounded in a humanitarian crisis. It was therefore not a surprise to see him presenting on the topic of how to accelerate completion of a project report and findings using a wiki based on Christopher Alexander’s Pattern Language work.
The idea of a pattern language appears to apply to any complex engineering task, and has been applied to some of them. It has been especially influential in software engineering where patterns have been used to document collective knowledge in the field.
This was a great example of non routine content aggregation via the coordinating mechanism of a wiki -from workshop to writeshop. ‘Building a collaborative knowledge product at the WHO’ was a session that showcased new thinking.
It’s only a game!
The previous week Andrzej led a Knowledge Cafe session on Gamification in a KM Environment. Once again this was an entertaining talk focusing on the psychology behind the use of games and especially the variety of user types (stakeholders) an organisation needs to consider and their motivations (the ‘\what”s in it for me’ again) for participating.
 Andrzej and I then led a working session where the delegates were asked this question:
Andrzej and I then led a working session where the delegates were asked this question:
what role (if any) do you see for gamification in KM?
The discussions were wide ranging: many were sceptical; some were  converts; others saw no role. But when asked to note down their top ideas this is what emerged:
converts; others saw no role. But when asked to note down their top ideas this is what emerged:
I was particularly drawn to the idea of surfacing expertise (which is how CapGemini where Andrzej is the Intranet supremo uses the technique) and the idea of using Gamification to demystify KM.
My take: Gamification is a big leap to make for senior executives who have not grown up in an online interactive environment. As Andrzej points out each one of us who uses LinkedIn is engaged in Gamification; ditto those of us with loyalty point cards. Its about how the technique is introduced that matters and where it is targeted.
A word or two from Dave Snowden
A few quotes from Dave’s opening address which I thought were spot on:
Danger of Community of Practice – correlation doesn’t give rise to causation.
@snowded prefers to talk about ‘decision support’ rather than ‘knowledge management’ – it describes what it does
Understanding the history of the organisation is a key to understanding its culture.
The idea of creating a big database of lessons (identified) only works if those are then fed back into the workings of the organisation – then they can be described as ‘Lessons Learned’! Most aren’t which is why the idea of a pool of case studies is often also a waste of time. Its rare for two cases in one organisation to be the same so why would you expect something that happens someone else to be a perfect fit for your own organisation.
And finally
Exactly!